Explain Metabolism of Different Organic Compounds
Sulphur dioxide gas and sodium chloride Organic compounds These are compounds made through chemical reactions in living organism. DCarbon flow is from carbon dioxide to organic compounds in lithotropic.

D And L Notation For Sugars Master Organic Chemistry Organic Chemistry Chemistry Organic Chemistry Study
SAR11 clade reduced the concentration of compounds.

. Inorganic compound These are compounds made by a natural geophysical process in the environment. Since metabolism and metabolites are the product of enzyme pathways and enzymes are encoded in genes the metabolic capabilities of a prokaryote are a reflection of its genome. Microbial metabolism is the means by which a microbe obtains the energy and nutrients eg.
They provide energy and form structures such as cell walls. Proteins lipids and carbohydrates are necessary to maintain various biological processes such as metabolism respiration and circulation in the blood. ATP organic compound ADP phosphorylated organic compound H.
Proteins lipids and carbohydrates are necessary to sustain biological processes such as metabolism respiration and blood circulation. For this metabolism to take place the compounds must enter plant tissues. Anabolism uses energy to make compounds.
A type of organic compound called nucleotide forms the amino acids and the DNA. Cofactors and minerals in metabolism. Phototrophs are organisms that use light as their source of energy to produce ATP and carry.
Another way that organisms extract energy from ATP is to energize organic compounds by transferring a phosphoryl group directly to the compound. Biodegradation or biological degradation is the phenomenon of biological transformation of organic compounds by living organisms particularly the microorganisms. The specific metabolic properties of a microbe are the major factors in determining that microbes.
A Carbon flow is from organic compounds to carbon dioxide in aeroboc metabolism. Require only CO 2 as a carbon source and obtain energy by oxidizing inorganic compounds. The process by which plants and other photoautotrophs generate carbohydrates and oxygen from carbon dioxide water and light energy in chloroplasts.
When there is adequate ATP present excess glucose is shunted into glycogen for storage. They store energy and help form cell membranes in addition to having other functions in organisms. CCarbon flow is flow organic compounds to fermentation products in anaerobic respiration.
This misinformation may arise from the way most textbooks explain energy metabolism emphasizing glycolysis the metabolic pathway for glucose. Cells have enzymes that help break those bonds to release the energy. In contrast man-made compounds also known as xenobiotics are often refractory to degradation.
Lipids are organic compounds such as fats and oils. This mode of nutrition is unique only to certain prokaryotes. There are many different environments on Earth with various energy and carbon sources and variable conditions to which prokaryotes may be able to adapt.
Generally hydrogen from organic compounds is released during pyrolysis at high temperature thus analyzing hydrogen requires a separate combustion. Water Carbon dioxide oxygen. Use light energy to synthesize organic compounds from CO2 Includes the cyanobacteria.
Actually all photosynthetic eukaryotes fit in this category 2. They form in living organisms as part of metabolism. Catabolism breaks down compounds to release their energy.
Lipids or fats store energy in the body for later use. Plant metabolism of organic compounds is a vital phytoremediation process for sustainable waste management. Biodegradation of naturally occurring organic compounds follows their synthesis.
Metabolism appears to follow detoxification or elimination metabolic processes which are collectively called the green-liver model. The main reason is that they cannot be recognized by naturally present organisms and therefore do not enter common metabolic pathways. The conversion of food to building blocks for proteins lipids nucleic acids and some carbohydrates.
An important enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of adenosine diphosphate into adenosine triphosphate. Carbon it needs to live and reproduceMicrobes use many different types of metabolic strategies and species can often be differentiated from each other based on metabolic characteristics. Plants and phytoplankton are natural sources of the volatile organic compounds VOCs acetone and isoprene which are reactive and can alter atmospheric chemistry.
Amino acid synthesis through reductive amination is intimately related to the process of aerobic respiration and organic acid metabolism. Glycogen a polymer of glucose is an energy-storage molecule in animals. It has unstable phosphate bonds that are easily broken.
During aerobic respiration the conversions of α-ketoglutaric acid to glutamic acid oxaloacetic acid to aspartic acid and pyruvic acid to alanine are considered as side reactions of Krebs cycle. Proteins are organic compounds made up of amino acids. A class of organic compounds called nucleotides form amino acids and DNA.
Therefore uptake of. How does ATP serve as a carrier of free energy. Biodegradation basically involves the conversion of complex organic.
The conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes. Carbohydrates give life forms the energy needed to maintain cellular function. In earlier research we reported that when co-cultured with a diatom the marine bacterium Pelagibacter strain HTCC1062.
Metabolism m ə ˈ t æ b ə l ɪ z ə m from Greek. μεταβολή metabolē change is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organismsThe three main purposes of metabolism are. Carbohydrates are organic compounds such as sugars and starches.
The organic compounds proteins lipids and carbohydrates contain the majority of the carbon and nitrogen in humans whereas most of the oxygen and hydrogen. In this reaction ATP is dephosphorylated and an organic compound is phosphorylated as shown in the reaction below. Organic compounds are composed of hydrogen oxygen and carbon atoms and are found in all life forms.
Glycogen from the liver and muscles hydrolyzed into glucose-1-phosphate together with fats and proteins can feed into the catabolic pathways for carbohydrates. BCarbon flow is from organic compounds to fermentation products in the anaerobic process of fermentation.

Hormonal Imbalance In Women How To Solve It Naturally Hormone Imbalance Hormones Hormone Imbalance Symptoms

Compound Interest On Twitter Chemistry Education Study Chemistry Chemistry Lessons

Cell Metabolism Learn Science At Scitable

Interactive Biochemical Pathways Of A Cell Metabolism Pathways Biochemistry

What Is Life Part Ii Biomolecules And The Genetic Code New Criticals Biology Classroom Biology Lessons Science Biology

Naming Organic Compounds Naming Organic Compounds Functional Group Methylation

What Is Urea What Is All Chemistry Urinal Chemistry Education

Calvin Benson Cycle Light Independent Reaction Dark Reaction Conversion Of Carbon Dioxide To Organic Compounds Plant Science Teaching Biology Biochemistry
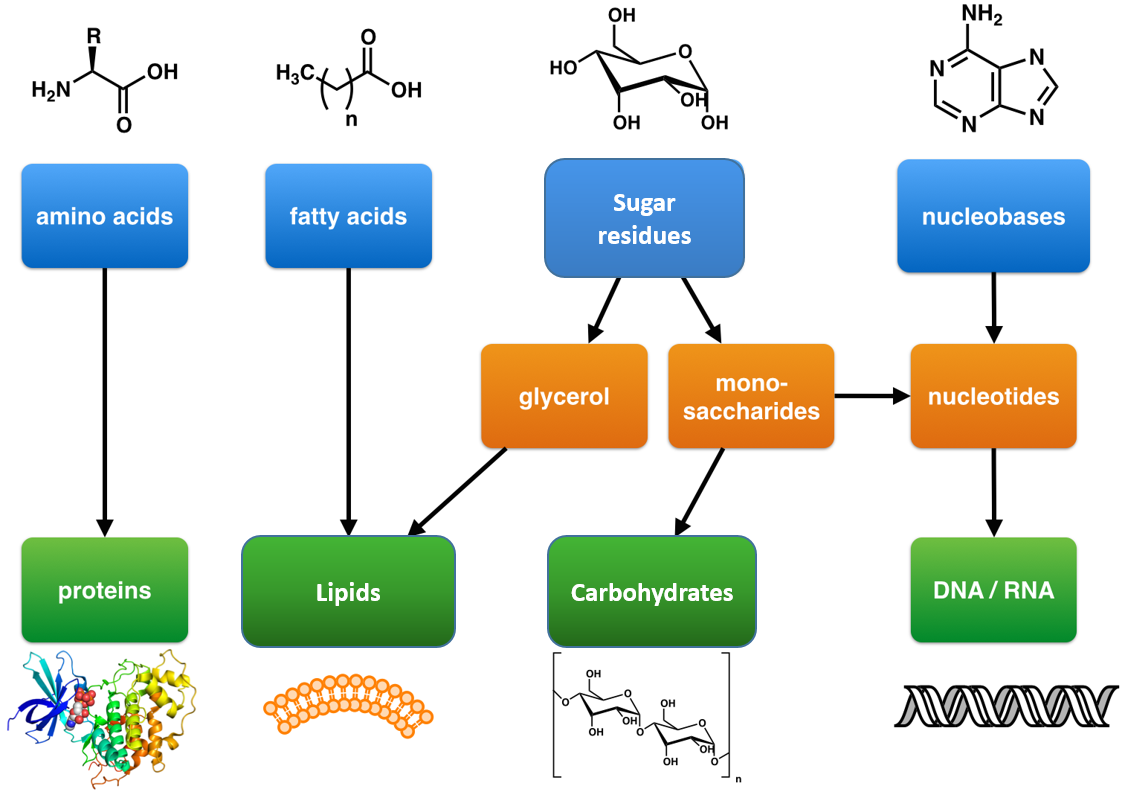
Ch105 Chapter 6 A Brief History Of Natural Products And Organic Chemistry Chemistry

Undeserved Reputation Aspartame The Artificial Sweetener Artificial Sweetener Teaching Chemistry Organic Chemistry

Pin On Hnfe 3025 Metabolic Nutrition

Overview Of Metabolic Reactions Anatomy And Physiology Ii

Metabolism Catabolism Vs Anabolism Macromolecules Biochemistry Microbiology Study
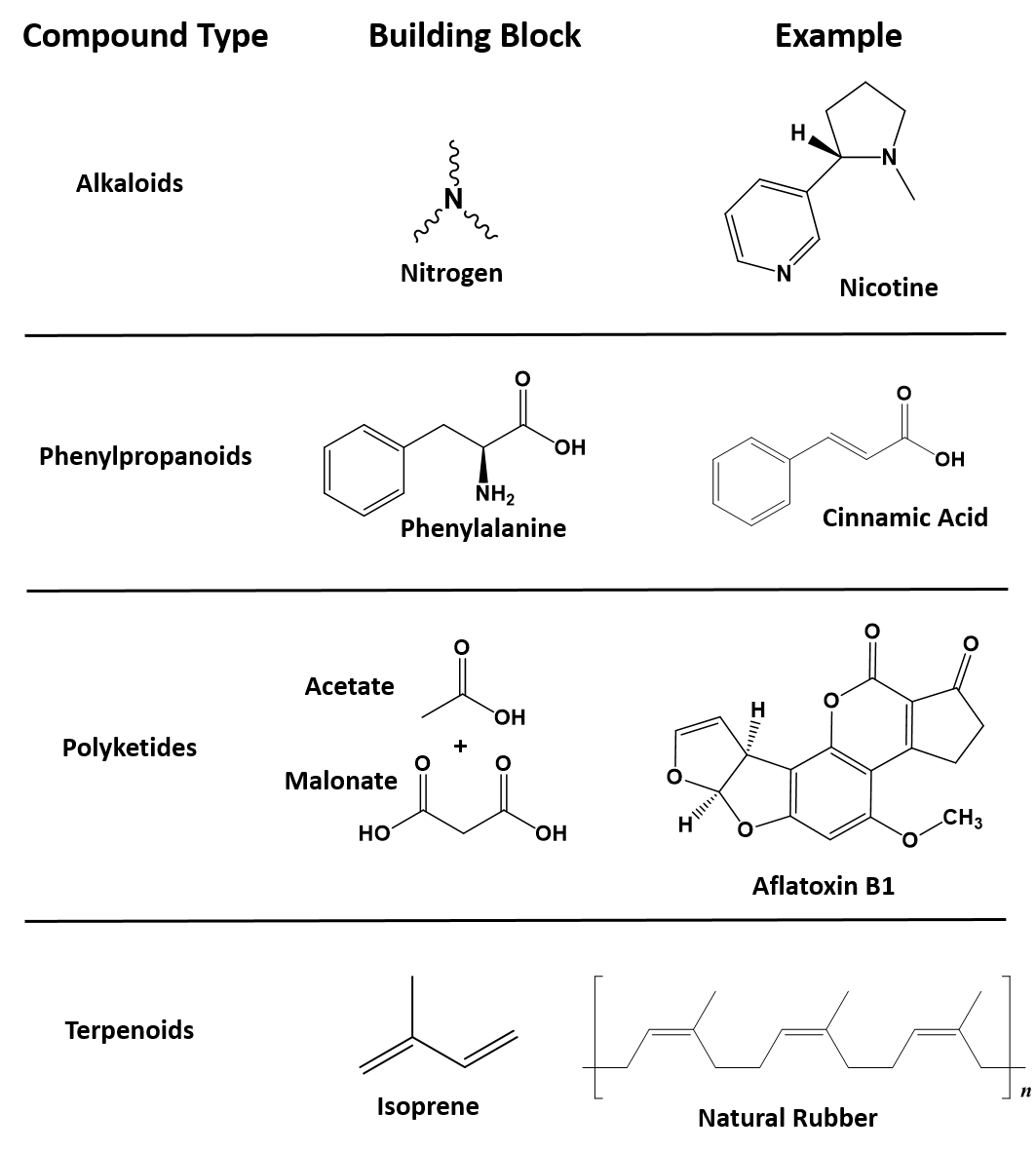
Ch105 Chapter 6 A Brief History Of Natural Products And Organic Chemistry Chemistry
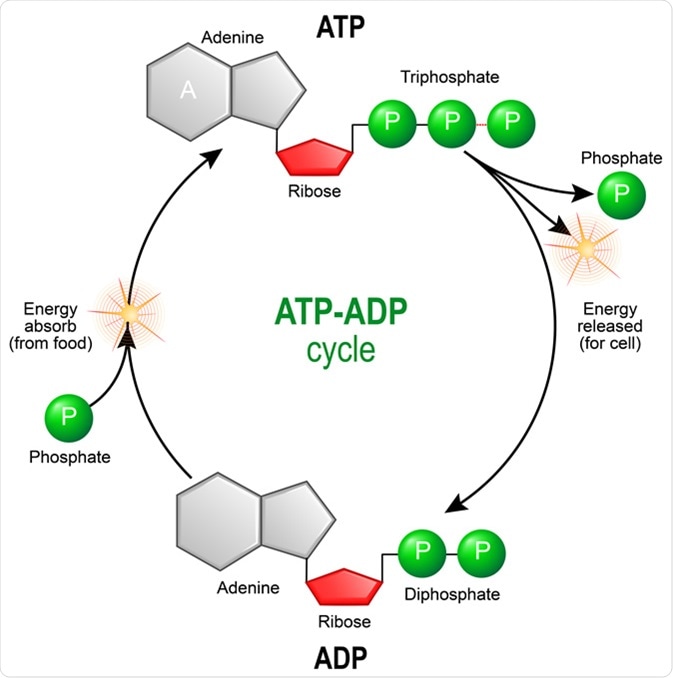




Comments
Post a Comment